The majority of patients who survive a stroke usually continue to suffer from permanent motor disorders (hemiparesis) or a linguistic handicap (aphasia). A study of the Department of Neurology of CHU Dinant Godinne — UCL Namur, reveals an improvement in the efficiency of the brain activity when patients receive a treatment combining motor revalidation with non-invasive brain stimulation. Demonstrated via the technique of functional MRI, these promising results are currently published in Brain, the British scientific journal dedicated to neurology.
Neuro-rehabilitation (physical therapy, occupational therapy, etc.) helps hemaparetic stroke patients confronted with loss of motor skills on one side of their body, to recover some of their motor functions after a cerebrovascular accident. One of the most promising tracks in neuro-rehabilitation consists in amplifying the motor learning ability after a stroke, in other words how to learn (again) how to make movements with the parts of the human body impacted after a stroke.
Pilot studies have shown at this matter that tDCS (transcranial direct current stimulation) — a non-invasive and painless cerebral stimulation method — allowed to modulate the cerebral activity and to increase the motor performances of patients who have been victim of stroke. This method consists of applying low voltage electric currents on the patient’s head by means of electrodes during short periods of time. In 2012, a first study conducted by the teams of Professors Yves Vandermeeren and Patrice Laloux allowed to demonstrate that tDCS amplified the motor learning and the long-term motor memory of the patient after a stroke. This study was awarded with the Fernand Depelchin Prize of the Université catholique de Louvain (UCL) and allowed the CHU Neurology Team to continue its research, in particular via the use of functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) of the brain.
Nineteen hemiparetic stroke patients (with a motor deficit in the upper limb) participated to this new clinical trial. In order to avoid study bias, the stimulations were performed in a double-blind, randomised fashion. Each patient received a real stimulation as well as a placebo-stimulation during two separate sessions. Because the tDCS was as good as completely imperceptible, it became impossible for patients to determine if they received a true or a placebo-stimulation.
During the first stimulation session (real or placebo), the patients learned how to perform a task with a paralyzed hand, combining speed and accuracy. One week later, they performed the learned task while the functional MRI scanner recorded their cerebral activity. After one week, this experience was completely done over again with the other stimulation (placebo or real).
As in the previous study, the non-invasive cerebral stimulation amplified the motor learning capacity with the paralyzed hand and the long-term memory retention in a spectacular way for patients with a chronic stroke.
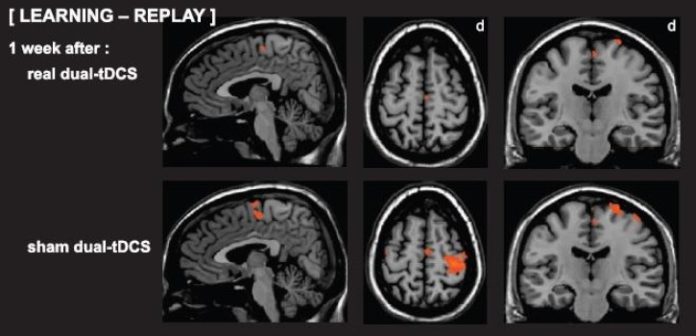
Thanks to functional MRI, this second study demonstrates that the combination of motor learning and non-invasive cerebral stimulation improves the efficiency of the cerebral activity. Indeed, one week after the placebo stimulation, the cerebral activations measured via the functional MRI was very diffuse. Large cerebral zones were somehow “recruited ” although motor performance was low (poor retention). On the other hand, one week after real stimulation, the cerebral activation was focused on the essential motor zones, almost identical to a person without stroke-impact although the motor performance was significantly better (enhanced task retention). In other words, the combination of motor learning and tDCS reinforced the essential motor zones and this specific network was reactivated one week after the real intervention.
For thousands of stroke victims, this study opens considerable perspectives in the domain of neuro-rehabilitation. A better understanding of the cerebral functioning after a stroke and how non-invasive cerebral stimulation works will help researchers to develop the neuro-rehabilitation of the future. The results of this study will be implemented within the consortium Louvain Bionics, inaugurated on November 12 of this year at UCL.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Université catholique de Louvain – UCL. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Journal Reference:
- S. Lefebvre, L. Dricot, P. Laloux, W. Gradkowski, P. Desfontaines, F. Evrard, A. Peeters, J. Jamart, Y. Vandermeeren. Neural substrates underlying stimulation-enhanced motor skill learning after stroke. Brain, 2014; DOI: 10.1093/brain/awu336