The development of a new organism from the joining of two single cells is a carefully orchestrated endeavor. But even before sperm meets egg, an equally elaborate set of choreographed steps must occur to ensure successful sexual reproduction. Those steps, known as reproductive cell division or meiosis, split the original number of chromosomes in half so that offspring will inherit half their genetic material from one parent and half from the other.
During meiosis, each set of homologous chromosomes pair up in a kind of chromosomal square dance, chromosome 1 with chromosome 1, 2 with 2, and so on down the line. The partners stick together, dancing through the phases of meiosis, until it is time to segregate or separate to opposite ends of the dividing cell. When the dancers don’t pair or part appropriately it can result in eggs and sperm with the wrong number of chromosomes, a major cause of miscarriage and birth defects.
To avoid these mistakes, most chromosomes use a process known as crossing over, looping their arms with their partners and even swapping pieces of genetic material to stick together until the dance is over. A few chromosomes, like chromosome 4 in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, are too short to make these crossovers. Yet somehow, they have figured out another way to stay connected to their partners.
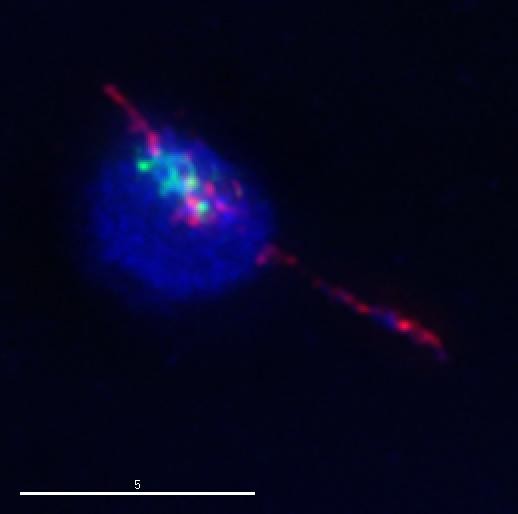
Previously, Stacie E. Hughes, Ph.D., a research specialist II at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research, identified thin threads of DNA that seemed to tie these other homologous chromosomes together. Yet a major question remained: once these chromosomes are roped into pairs, how do they manage to come apart again?
Now, Hughes and R. Scott Hawley, Ph.D., have shown that an enzyme called Topoisomerase II is required for resolving these threads so homologous chromosomes can part ways. The finding, published in the October 23, 2014 issue of PLoS Genetics, underscores the complexity of the meiotic process.
“It is not surprising there are many ways to segregate chromosomes because there are also many ways to control other molecular events, like gene expression,” says Hawley, a Stowers Institute investigator and American Cancer Society research professor. “This method of segregating shorter chromosomes may be clunky, odd, crazy, and as noncanonical as it gets, but that doesn’t matter, because the cells survive. In the end, these processes don’t have to be elegant, they just have to work.”
Ever since Hughes’ initial discovery of DNA threads, she and Hawley have been looking for the molecular scissors responsible for cutting entangled chromosomes free. The most prominent candidate to emerge from their search was Topoisomerase II, an enzyme known to cut and untwist tangled strands of the double helix.
Previous research had shown that Topisomerase II was involved in earlier cellular processes like DNA replication, and the enzyme was still detectable even during later phases of meiosis. The researchers thought that Topoisomerase II might be waiting around to do yet another job, cutting DNA threads to allow homologous chromosomes to segregate.
Testing their hypothesis seemed relatively straightforward. The researchers simply needed to “knock out” Topoisomerase II in their model organism of choice — the female fruit fly — and then look to see whether meiosis was able to proceed normally without it. However, because the enzyme was involved in so many critical cellular processes, the researchers knew that such an approach would yield nothing more than dead fruit flies.
Instead, they adapted a sophisticated method known as RNA interference — which uses small pieces of DNA’s chemical cousin RNA to silence genes — and eliminated Topoisomerase II at a specific time point late in meiosis. Hughes then isolated the oocytes from the fruit flies and analyzed them using fluorescent tags that illuminate the DNA threads connecting the chromosomes. Their findings were dramatic.
“Without this enzyme the chromosomes can’t come apart, they are stuck together like glue,” says Hughes. “There are large regions of the chromosomes that are tethered together by these threads, while the rest is stretched out like a slinky as the chromosomes are pulled in opposite directions. It is just a mess. Because the chromosomes are just stuck there, they can’t finish meiosis.”
As a result, the mutant flies are essentially sterile. A separate study published in the same journal shows that male mutants experience a similar fate, their spermatocytes permanently locked in an immature state. Without Topoisomerase II, the oocytes and spermatocytes are locked in meiosis, unable to complete the next steps — fertilization, cell division and differentiation — needed to create a new organism.
The work was funded in part by the Stowers Institute for Medical Research and the American Cancer Society (award number RP-05-086-06-DDC).
Summary of Findings
During the formation of eggs and sperm, the cell’s chromosomes must pair up and part in an elaborate sequence that results in sex cells with exactly half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. A single misstep can cause infertility, miscarriage, and birth defects. Recent research has shown that some chromosomes avoid these mistakes by using thin threads of DNA to tether themselves together, but how they come untied again has not been clear. In the current issue of the scientific journal PLoS Genetics, Stowers Institute scientists report that an enzyme called Topoisomerase II is required for these entangled chromosomes to be set free. Stowers Research Associate II Stacie E. Hughes, Ph.D., who led the study, explains that without the enzyme, female fruit flies were unable to complete meiosis and were rendered completely sterile. Topoisomerase II likely resolves the DNA entanglements by cutting and untwisting tangled DNA, as in other processes like DNA replication.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Stowers Institute for Medical Research. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Journal Reference:
- Stacie E. Hughes, R. Scott Hawley. Topoisomerase II Is Required for the Proper Separation of Heterochromatic Regions during Drosophila melanogaster Female Meiosis. PLoS Genetics, 2014; 10 (10): e1004650 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004650