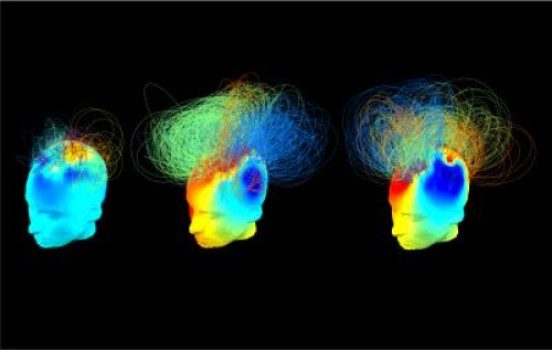
Scientists in Cambridge have found hidden signatures in the brains of people in a vegetative state, which point to networks that could support consciousness even when a patient appears to be unconscious and unresponsive. The study could help doctors identify patients who are aware despite being unable to communicate.
There has been a great deal of interest recently in how much patients in a vegetative state following severe brain injury are aware of their surroundings. Although unable to move and respond, some of these patients are able to carry out tasks such as imagining playing a game of tennis. Using a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanner, which measures brain activity, researchers have previously been able to record activity in the pre-motor cortex, the part of the brain which deals with movement, in apparently unconscious patients asked to imagine playing tennis.
Now, a team of researchers led by scientists at the University of Cambridge and the MRC Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit, Cambridge, have used high-density electroencephalographs (EEG) and a branch of mathematics known as ‘graph theory’ to study networks of activity in the brains of 32 patients diagnosed as vegetative and minimally conscious and compare them to healthy adults. The findings of the research are published today in the journal PLOS Computational Biology. The study was funded mainly by the Wellcome Trust, the National Institute of Health Research Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre and the Medical Research Council (MRC).
The researchers showed that the rich and diversely connected networks that support awareness in the healthy brain are typically — but importantly, not always — impaired in patients in a vegetative state. Some vegetative patients had well-preserved brain networks that look similar to those of healthy adults — these patients were those who had shown signs of hidden awareness by following commands such as imagining playing tennis.
Dr Srivas Chennu from the Department of Clinical Neurosciences at the University of Cambridge says: “Understanding how consciousness arises from the interactions between networks of brain regions is an elusive but fascinating scientific question. But for patients diagnosed as vegetative and minimally conscious, and their families, this is far more than just an academic question — it takes on a very real significance. Our research could improve clinical assessment and help identify patients who might be covertly aware despite being uncommunicative.”
The findings could help researchers develop a relatively simple way of identifying which patients might be aware whilst in a vegetative state. Unlike the ‘tennis test’, which can be a difficult task for patients and requires expensive and often unavailable fMRI scanners, this new technique uses EEG and could therefore be administered at a patient’s bedside. However, the tennis test is stronger evidence that the patient is indeed conscious, to the extent that they can follow commands using their thoughts. The researchers believe that a combination of such tests could help improve accuracy in the prognosis for a patient.
Dr Tristan Bekinschtein from the MRC Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit and the Department of Psychology, University of Cambridge, adds: “Although there are limitations to how predictive our test would be used in isolation, combined with other tests it could help in the clinical assessment of patients. If a patient’s ‘awareness’ networks are intact, then we know that they are likely to be aware of what is going on around them. But unfortunately, they also suggest that vegetative patients with severely impaired networks at rest are unlikely to show any signs of consciousness.”
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of Cambridge. The original story is licensed under a Creative Commons Licence. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Journal Reference:
- Chennu S, Finoia P, Kamau E, Allanson J, Williams GB, et al. Spectral Signatures of Reorganised Brain Networks in Disorders of Consciousness. PLOS Computational Biology, 2014; 10 (10): e1003887 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003887