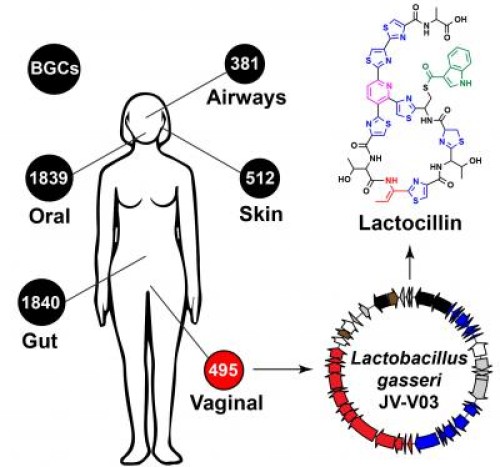
Bacteria that normally live in and upon us have genetic blueprints that enable them to make thousands of molecules that act like drugs, and some of these molecules might serve as the basis for new human therapeutics, according to UC San Francisco researchers who report their new discoveries in the September 11, 2014 issue of Cell.
The scientists purified and solved the structure of one of the molecules they identified, an antibiotic they named lactocillin, which is made by a common bacterial species, Lactobacillus gasseri, found in the microbial community within the vagina. The antibiotic is closely related to others already being tested clinically by pharmaceutical companies. Lactocillin kills several vaginal bacterial pathogens, but spares species known to harmlessly dwell in the vagina.
This example suggests that there may be an important role for many naturally occurring drugs — made by our own microbes — in maintaining human health, said the senior author of the study, Michael Fischbach, PhD, an assistant professor of bioengineering with the UCSF School of Pharmacy, who has established a career discovering interesting molecules made by microbes.
“We used to think that drugs were developed by drug companies, approved by the FDA, and prescribed by physicians, but we now think there are many drugs of equal potency and specificity being produced by the human microbiota,” Fischbach said.
About a third of all medicines used in the clinic are derived from microbes and plants, Fischbach said. These include antibiotics like penicillin, numerous drugs used in cancer chemotherapy, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. Although those who prospect for drugs from microbes have been combing the depths of the oceans and probing exotic soils around the globe, only now have scientists begun to look within our own bodies.
There are hundreds of bacterial species associated with each of us, and thousands of distinct strains among them. We do not all harbor the same species, and different species are found at different body sites.
Through research funded by the National Institutes of Health’s Human Microbiome Project and other studies, scientists in recent years have begun to describe the microbiomes — ecosystems made up of many microbial species — found in the gut, skin, nasal passages, mouth and vagina.
They have started to identify microbiomes in which species diversity and abundance differ from the normal range in ways that are associated with disease risks. However, the identification of molecules that govern interactions between microbes and their human hosts has lagged; only a handful have been identified, Fischbach said.
By developing new data-analysis software and putting it to work on an extensive genetic database developed from human-associated bacterial samples collected as part of the ongoing Human Microbiome Project, Fischbach’s lab team identified clusters of bacterial genes that are switched-on in a coordinated way to guide the production of molecules that are biologically active in humans.
Like language-translation programs, the mathematical algorithm Fischbach’s team developed, called ClusterFinder, uses machine-learning principals to draw conclusions from new data, based on what is already known — in this case previously identified relationships between gene clusters in soil and marine bacterial species and the molecules they produce.
Using ClusterFinder, Fischbach’s team for the first time systematically analyzed genomes from microbiome species and data on gene activity from human samples to identify 3,118 distinct clusters of bacterial genes that are found in various human body sites. The gene clusters his team identified encode enzymes that serve as molecular factories to produce specific drug-like molecules that fit into known classes of pharmaceuticals.
The new study reveals that the genus-level analysis commonly used to identify bacteria within human microbiomes is not detailed enough to predict which drug-like molecules the bacteria make, Fischbach said. Individual species, and different strains within each species, differ in the molecules they produce.
“We need to learn what these molecules are and what they are doing,” Fischbach said. “This could represent a pool of molecules with many tantalizing candidates for drug therapy.
“It’s been clear for several years that variations and changes in the human microbiome have interesting effects on the human host, and now we can begin to determine why this is true on a molecular level.”
UCSF postdoctoral fellow Mohamed S. Donia, PhD, designed and conducted key experiments and took the lead in drafting the newly published study. Other co-authors include UCSF postdoctoral fellow Peter Cimermancic, PhD; postdoctoral fellow Christopher J. Schulze, PhD, from Stanford University; associate professor Roger G. Linington, PhD, from UC Santa Cruz; chemistry lecturer Laura C. Wieland Brown, PhD, from Indiana University; John Martin and Makedonka Mitreva, PhD, assistant professor, from Washington University, St. Louis; and Jon Clardy, PhD, professor at Harvard Medical School.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, the W.M. Keck Foundation, the David and Lucile Packard Foundation and the UCSF Program for Breakthrough Biomedical Research. Fischbach is on the scientific advisory boards of NGM Biopharmaceuticals and Warp Drive Bio.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of California, San Francisco. The original article was written by Jeffrey Norris. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Journal Reference:
- Mohamed S. Donia, Peter Cimermancic, Christopher J. Schulze, Laura C. Wieland Brown, John Martin, Makedonka Mitreva, Jon Clardy, Roger G. Linington, Michael A. Fischbach. A Systematic Analysis of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in the Human Microbiome Reveals a Common Family of Antibiotics. Cell, 2014; 158 (6): 1402 DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.032